EN
Node.js - PostgreSQL AVG()
0
points
In this article, we would like to show you how to use SQL AVG() function in Node.js.
Note: at the end of this article you can find database preparation SQL queries.
Example 1
const { Client } = require('pg');
const client = new Client({
host: '127.0.0.1',
user: 'postgres',
database: 'database_name',
password: 'password',
port: 5432,
});
const execute = async (query) => {
try {
await client.connect(); // gets connection
const { rows } = await client.query(query); // sends query
console.log(rows);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error.stack);
} finally {
await client.end(); // closes connection
}
};
execute('SELECT AVG("salary") FROM "users"');
Output:
[ { 'AVG(`salary`)': 3631.25 } ]
Example 2
const { Client } = require('pg');
const client = new Client({
host: '127.0.0.1',
user: 'postgres',
database: 'dirask',
password: 'password',
port: 5432,
});
const execute = async (query) => {
try {
await client.connect(); // gets connection
const { rows } = await client.query(query); // sends queries
console.table(rows);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error.stack);
} finally {
await client.end(); // closes connection
}
};
const text = `SELECT * FROM "users"
WHERE "salary" < (SELECT AVG("salary") FROM "users")`;
execute(text);
Output:
┌─────────┬────┬──────────┬────────────┬───────────────┬───────────┐
│ (index) │ id │ name │ surname │ department_id │ salary │
├─────────┼────┼──────────┼────────────┼───────────────┼───────────┤
│ 0 │ 1 │ 'John' │ 'Stewart' │ 1 │ '3512.00' │
│ 1 │ 2 │ 'Chris' │ 'Brown' │ 2 │ '1344.00' │
│ 2 │ 6 │ 'Simon' │ 'Collins' │ 4 │ '3320.00' │
│ 3 │ 7 │ 'Taylor' │ 'Martin' │ 2 │ '1500.00' │
│ 4 │ 8 │ 'Andrew' │ 'Thompson' │ null │ '2100.00' │
└─────────┴────┴──────────┴────────────┴───────────────┴───────────┘
Database preparation
create_tables.sql file:
CREATE TABLE "users" (
"id" SERIAL,
"name" VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
"surname" VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
"department_id" INTEGER,
"salary" DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ("id")
);
insert_data.sql file:
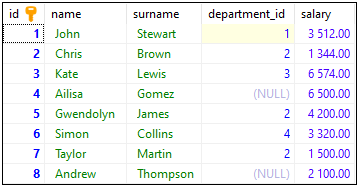
INSERT INTO "users"
( "name", "surname", "department_id", "salary")
VALUES
('John', 'Stewart', 1, '3512.00'),
('Chris', 'Brown', 2, '1344.00'),
('Kate', 'Lewis', 3, '6574.00'),
('Ailisa', 'Gomez', NULL, '6500.00'),
('Gwendolyn', 'James', 2, '4200.00'),
('Simon', 'Collins', 4, '3320.00'),
('Taylor', 'Martin', 2, '1500.00'),
('Andrew', 'Thompson', NULL, '2100.00');