EN
Node.js - PostgreSQL CASE statement
0
points
In this article, we would like to show you how to use Postgres CASE statement in Node.js.
Note: at the end of this article you can find database preparation SQL queries.
const { Client } = require('pg');
const client = new Client({
host: '127.0.0.1',
user: 'postgres',
database: 'database_name',
password: 'password',
port: 5432,
});
const getSalaryOverview = async () => {
const query = `
SELECT "name", "salary",
CASE
WHEN "salary" > 6000 THEN 'Salary greater than 6000$'
WHEN "salary" > 4000 THEN 'Salary greater than 4000$'
WHEN "salary" >= 2000 THEN 'Salary greater than 2000$'
ELSE 'Salary less than 2000$'
END AS "Salary information"
FROM "users";`;
try {
await client.connect(); // gets connection
const { rows } = await client.query(query); // sends query
console.table(rows);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error.stack);
} finally {
await client.end(); // closes connection
}
};
getSalaryOverview();
Result:
┌─────────┬─────────────┬───────────┬─────────────────────────────┐
│ (index) │ name │ salary │ Salary information │
├─────────┼─────────────┼───────────┼─────────────────────────────┤
│ 0 │ 'John' │ '3512.00' │ 'Salary greater than 2000$' │
│ 1 │ 'Chris' │ '1344.00' │ 'Salary less than 2000$' │
│ 2 │ 'Kate' │ '6574.00' │ 'Salary greater than 6000$' │
│ 3 │ 'Ailisa' │ '6500.00' │ 'Salary greater than 6000$' │
│ 4 │ 'Gwendolyn' │ '4200.00' │ 'Salary greater than 4000$' │
│ 5 │ 'Simon' │ '3320.00' │ 'Salary greater than 2000$' │
│ 6 │ 'Taylor' │ '1500.00' │ 'Salary less than 2000$' │
│ 7 │ 'Andrew' │ '2100.00' │ 'Salary greater than 2000$' │
└─────────┴─────────────┴───────────┴─────────────────────────────┘
Database preparation
create_tables.sql file:
CREATE TABLE "users" (
"id" SERIAL,
"name" VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
"surname" VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
"department_id" INTEGER,
"salary" DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ("id")
);
insert_data.sql file:
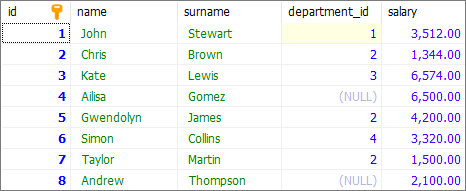
INSERT INTO "users"
( "name", "surname", "department_id", "salary")
VALUES
('John', 'Stewart', 1, '3512.00'),
('Chris', 'Brown', 2, '1344.00'),
('Kate', 'Lewis', 3, '6574.00'),
('Ailisa', 'Gomez', NULL, '6500.00'),
('Gwendolyn', 'James', 2, '4200.00'),
('Simon', 'Cousersllins', 4, '3320.00'),
('Taylor', 'Martin', 2, '1500.00'),
('Andrew', 'Thompson', NULL, '2100.00');
Native SQL query (used in the above example):
SELECT `name`, `salary`,
CASE
WHEN `salary` > 6000 THEN 'Salary greater than 6000$'
WHEN `salary` > 4000 THEN 'Salary greater than 4000$'
WHEN `salary` >= 2000 THEN 'Salary greater than 2000$'
ELSE 'Salary less than 2000$'
END AS 'Salary information'
FROM `users`;