DE
JavaScript - Math.random() Methode - Beispiel
3
points
Die Math.random() Funktion gibt eine Gleitkomma-, Pseudozufallszahl zwischen dem Bereich [0,1), 0 (einschließlich) und 1 (exklusiv). Basierend auf dieser Funktion kann man Zufallszahlen im Bereich erhalten, wie man in den folgenden Beispielen sehen kann.
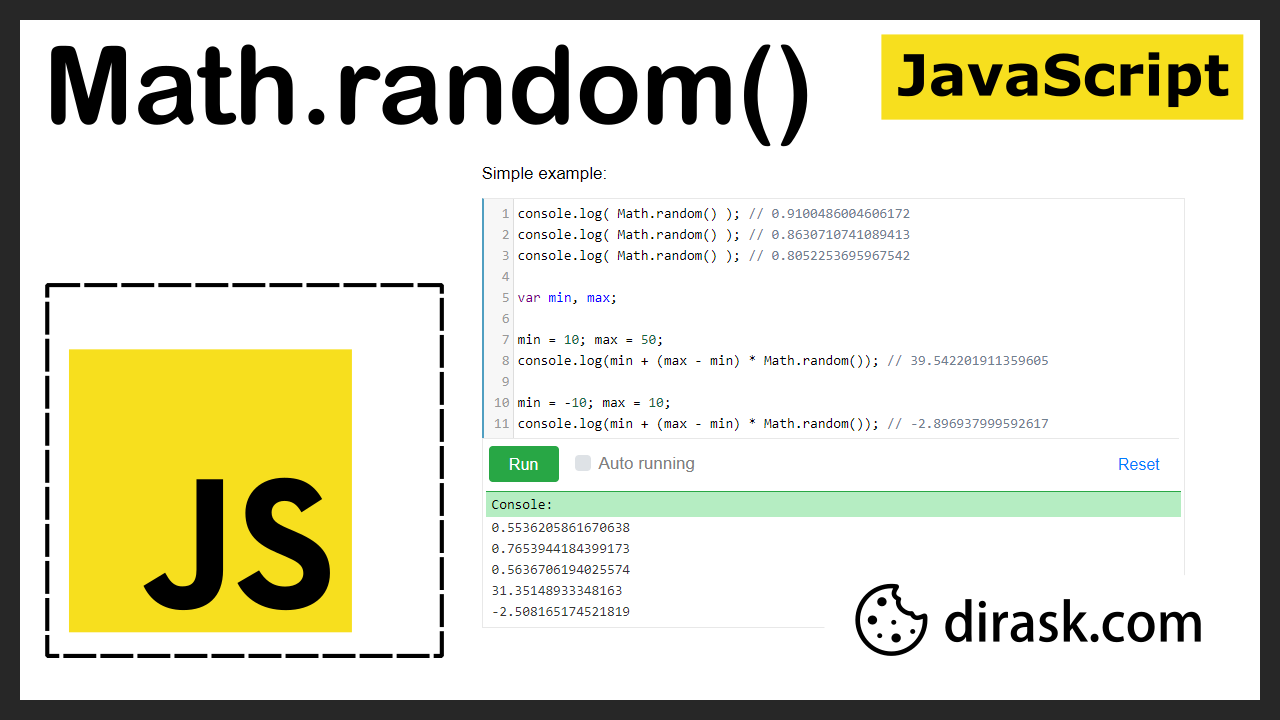
Einfaches Verwendungsbeispiel:
// ONLINE-RUNNER:browser;
console.log( Math.random() ); // 0.9100486004606172
console.log( Math.random() ); // 0.8630710741089413
console.log( Math.random() ); // 0.8052253695967542
function randomInt(min, max) {
return min + Math.floor((max - min) * Math.random());
}
function randomFloat(min, max) {
return min + (max - min) * Math.random();
}
console.log( randomInt( 10, 20) ); // 12
console.log( randomInt(-10, 10) ); // -4
console.log( randomFloat( 10, 20) ); // 14.514897223860018
console.log( randomFloat(-10, 10) ); // -6.645075993092653
1. Dokumentation
| Syntax | Math.random() |
| Parameter | Diese Methode akzeptiert keine Argumente. |
| Ergebnis | Gleitkommanumberwert (primitiver Wert). |
| Beschreibung | random ist eine statische Methode, die eine zufällige Gleitkommazahl aus dem Bereich <0, 1) - einschließlich 0 und exklusiv 1 - zurückgibt. |
2. Benutzerdefinierte Zufallsmethoden - Beispiel
2.1. Zufälliges Float im Bereich (exklusiver Maximalwert)
Dieses Beispiel zeigt, wie man Zufallszahlen mit der exklusiven max. randomzeFloat() Methode auf folgende Weise überschreiben:
randomzeFloat()- generiert Zahlen im Bereich von0bisNumber.MAX_VALUE(exklusiv),randomzeFloat(max)- generiert Zahlen im Bereich von0bismax(exklusiv) -maxWert muss positiv sein,randomzeFloat(min, max)- generiert Zahlen im Bereich vonminbismax(exklusiv).
// ONLINE-RUNNER:browser;
/*
inklusive min (Ergebnis kann gleich min Wert sein)
exklusive max (Ergebnis entspricht dem max Wert nicht)
*/
function randomizeFloat(min, max) {
if (max == null) {
if (min <= 0) {
throw new Error('Max value must be positive.');
}
max = (min == null ? Number.MAX_VALUE : min);
min = 0.0;
}
if (min >= max) {
throw new Error("Incorrect arguments.");
}
return min + (max - min) * Math.random();
}
// Beispiel:
console.log(randomizeFloat()); // 1.67319916301163e+308
console.log(randomizeFloat(5)); // 2.7593705936801918
console.log(randomizeFloat(10, 80)); // 37.54521514384005
console.log(randomizeFloat(-50, 50)); // -30.632843429520975
2.2. Zufälliges Float im Bereich (einschließlich Maximalwert) - Beispiel
// ONLINE-RUNNER:browser;
// generiert Werte aus <0, 1>
function randomizeValue() {
var value = (1 + 10E-16) * Math.random();
if (value > 1.0) {
return 1.0;
}
return value;
}
/*
inklusive min (Ergebnis kann gleich min Wert sein)
inklusive max (Ergebnis entspricht dem Maximalwert nicht)
*/
function randomizeFloat(min, max) {
if(max == null) {
max = (min == null ? Number.MAX_VALUE : min);
min = 0.0;
}
if(min >= max) {
throw new Error("Incorrect arguments.");
}
return min + (max - min) * randomizeValue();
}
// Beispiel:
console.log(randomizeFloat()); // 1.1960373039711962e+308
console.log(randomizeFloat(5)); // 0.7663988388633522
console.log(randomizeFloat(10, 80)); // 67.81113931017913
console.log(randomizeFloat(-50, 50)); // -13.713816892801674
2.3. Zufällige Ganzzahl im Bereich (exklusiver Maximalwert) - Beispiel
// ONLINE-RUNNER:browser;
/*
inklusive min (Ergebnis kann gleich min Wert sein)
exklusive max (Ergebnis entspricht dem Maximalwert nicht)
*/
function randomizeInteger(min, max) {
if(max == null) {
max = (min == null ? Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER : min);
min = 0;
}
min = Math.ceil(min); // inklusive min
max = Math.floor(max); // exklusive max
if(min > max - 1) {
throw new Error("Incorrect arguments.");
}
return min + Math.floor((max - min) * Math.random());
}
// Beispiel:
console.log(randomizeInteger()); // 5547382624322139
console.log(randomizeInteger(5)); // 3
console.log(randomizeInteger(10, 80)); // 62
console.log(randomizeInteger(-50, 50)); // -8
2.4. Zufällige Ganzzahl im Bereich (einschließlich Maximalwert) - Beispiel
// ONLINE-RUNNER:browser;
/*
inklusive min (Ergebnis kann gleich min Wert sein)
inklusive max (Ergebnis entspricht dem Maximalwert nicht)
*/
function randomizeInteger(min, max) {
if(max == null) {
max = (min == null ? Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER : min);
min = 0;
}
min = Math.ceil(min); // inklusive min
max = Math.floor(max); // exklusive max
if(min > max - 1) {
throw new Error("Incorrect arguments.");
}
return min + Math.floor((max - min + 1) * Math.random());
}
// Beispiel:
console.log(randomizeInteger()); // 5918572174489812
console.log(randomizeInteger(5)); // 5
console.log(randomizeInteger(10, 80)); // 60
console.log(randomizeInteger(-50, 50)); // -15
Literaturverzeichnis
- Zufallszahlengenerator - Wikipedia ENG
- Pseudozufallszahlengenerator - Wikipedia
- Liste von Zufallszahlengeneratoren - Wikipedia
Miniaturansicht