EN
MS SQL Server - Right Join
0
points
In this article, we would like to show you how to use RIGHT JOIN in MS SQL Server.
Quick solution:
SELECT [column1], [column2], [columnN]
FROM [table1]
RIGHT JOIN [table2]
ON [table1].[column_name] = [table2].[column_name];
Practical example
To show how the RIGHT JOIN works, we will use the following tables:
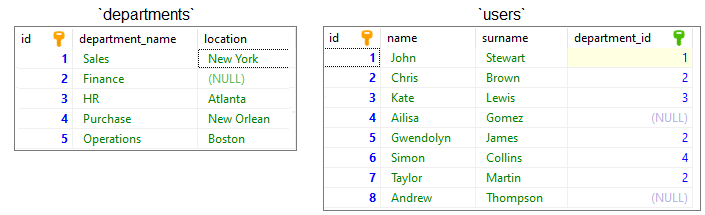
Note:
At the end of this article you can find databases preparation SQL queries.
Example
In this example, we will select all information about users and departments, even when there are no users assigned to a department.
Query:
SELECT * FROM [users]
RIGHT JOIN [departments]
ON [departments].[id] = [users].[department_id];
Output:
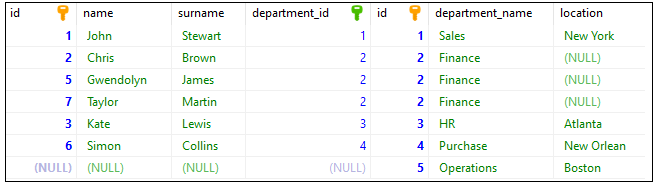
Database preparation
create_tables.sql file:
CREATE TABLE [departments] (
[id] INT NOT NULL,
[department_name] VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
[location] VARCHAR(50) NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ([id])
);
CREATE TABLE [users] (
[id] INT IDENTITY(1,1),
[name] VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
[surname] VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
[department_id] INT,
PRIMARY KEY ([id]),
FOREIGN KEY ([department_id]) REFERENCES [departments] ([id])
);
insert_data.sql file:
INSERT INTO [departments]
([id], [department_name], [location])
VALUES
(1, 'Sales', 'New York'),
(2, 'Finance', NULL),
(3, 'HR', 'Atlanta'),
(4, 'Purchase', 'New Orlean'),
(5, 'Operations', 'Boston');
INSERT INTO [users]
( [name], [surname], [department_id])
VALUES
('John', 'Stewart', 1),
('Chris', 'Brown', 2),
('Kate', 'Lewis', 3),
('Ailisa', 'Gomez', NULL),
('Gwendolyn', 'James', 2),
('Simon', 'Collins', 4),
('Taylor', 'Martin', 2),
('Andrew', 'Thompson', NULL);