EN
MS SQL Server - WHERE clause
0
points
In this article, we would like to show you how to use WHERE clause in MS SQL Server.
Quick solution:
SELECT [column1], [column2], ...
FROM [table_name]
WHERE condition;
Practical example
To show how the WHERE clause works, we will use the following table:
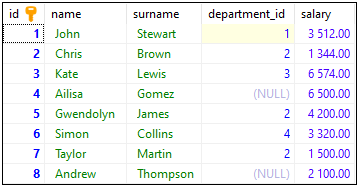
Note:
At the end of this article you can find database preparation SQL queries.
Example 1
In this example, we will display information about every user whose salary is greater than 3000.
Query:
SELECT * FROM [users] WHERE [salary] > 3000;
Output:
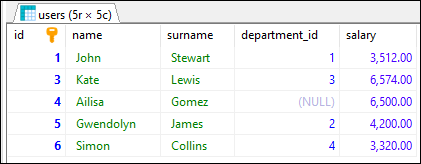
Example 2
In this example, we will display information about every user whose name is John.
Query:
SELECT * FROM [users] WHERE [name] = 'John';
Output:
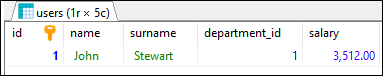
Note:
MS SQL Server requires single or double quotes (
'text'/"text") around text values.
Database preparation
create_tables.sql file:
CREATE TABLE [users] (
[id] INT IDENTITY(1,1),
[name] VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
[surname] VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
[department_id] INT,
[salary] DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ([id])
);
insert_data.sql file:
INSERT INTO [users]
( [name], [surname], [department_id], [salary])
VALUES
('John', 'Stewart', 1, '3512.00'),
('Chris', 'Brown', 2, '1344.00'),
('Kate', 'Lewis', 3, '6574.00'),
('Ailisa', 'Gomez', NULL, '6500.00'),
('Gwendolyn', 'James', 2, '4200.00'),
('Simon', 'Collins', 4, '3320.00'),
('Taylor', 'Martin', 2, '1500.00'),
('Andrew', 'Thompson', NULL, '2100.00');