EN
MS SQL Server - LIKE operator
0
points
In this article, we would like to show you how to use LIKE operator in MS SQL Server.
Quick solution:
SELECT [column_1], [column_2], [column_3], [column_n]
FROM [table_name]
WHERE [column_n] LIKE 'pattern'; /* or any other column */
We use LIKE operator in a WHERE clause to find rows that contan column cell that matches indicated pattern.
There are two wildcards used with the LIKE operator:
%- matches 0 or more characters (0, 1, 2, 3, ...),_- matches any single character (requres in_place some character).
| LIKE operator | Description |
|---|---|
| Finds any rows that username cell starts with prefix text. |
| Finds any rows that username cell ends with postfix text. |
| Finds any rows that username cell has middle text somewhere inside. |
|
Finds any rows that
|
Practical example
Let's say we have users database that contains usernames.
Listed patterns are matched with presented example texts:
PATTERN EXAMPLE MATCHED TEXTS
J% John J Jooohn etc.
Jo% John Jo Jooohn etc.
%n John n an etc.
%hn John hn ahn etc.
%h% John h aha etc.
%oh% John oh aoha etc.
J___ John Jaaa Jbbb etc.
Jo__ John Joaa Jobb etc.
___n John aaan bbbn etc.
__hn John aahn bbhn etc.
_oh_ John aoha bohb etc.
To show how the LIKE operator works, we will use the following table:
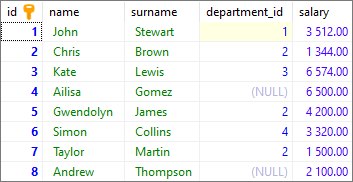
Note:
At the end of this article you can find database preparation SQL queries.
Example
In this example, we will display Jonh user row using some LIKE operator cases taken from above patterns.
Queries:
SELECT *
FROM [users]
WHERE [name] LIKE 'J%';
SELECT *
FROM [users]
WHERE [name] LIKE 'Jo%';
SELECT *
FROM [users]
WHERE [name] LIKE '%hn';
SELECT *
FROM [users]
WHERE [name] LIKE '_oh_';
SELECT *
FROM [users]
WHERE [name] LIKE 'J_h%';
Result:
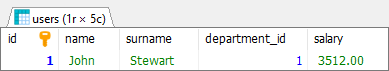
Database preparation
create_tables.sql file:
CREATE TABLE [users] (
[id] INT IDENTITY(1,1),
[name] VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
[surname] VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
[department_id] INT,
[salary] DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ([id])
);
insert_data.sql file:
INSERT INTO [users]
( [name], [surname], [department_id], [salary])
VALUES
('John', 'Stewart', 1, '3512.00'),
('Chris', 'Brown', 2, '1344.00'),
('Kate', 'Lewis', 3, '6574.00'),
('Ailisa', 'Gomez', NULL, '6500.00'),
('Gwendolyn', 'James', 2, '4200.00'),
('Simon', 'Collins', 4, '3320.00'),
('Taylor', 'Martin', 2, '1500.00'),
('Andrew', 'Thompson', NULL, '2100.00');