EN
MS SQL Server - Full Outer Join
0
points
In this article, we would like to show you how to do FULL OUTER JOIN in MS SQL Server.
Quick solution:
SELECT * FROM [table1]
FULL JOIN [table2] ON [table2].[column_name] = [table1].[column_name]
Note:
You might as well write
FULL JOINinstead ofFULL OUTER JOIN.
Practical example
To show how the FULL OUTER JOIN works, we will use the following tables:
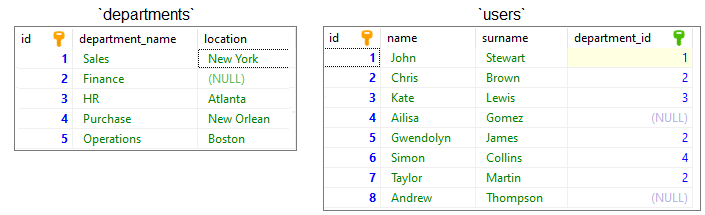
Note:
At the end of this article you can find databases preparation SQL queries.
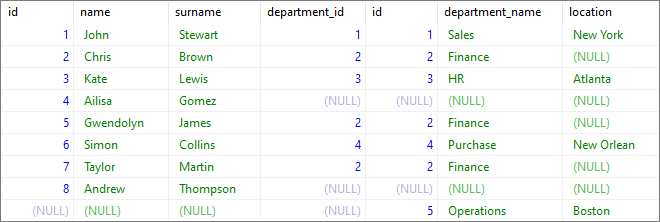
Example
In this example, we will select all information about users and departments.
Query:
SELECT *
FROM [users]
FULL JOIN [departments] ON [departments].[id] = [users].[department_id]
Output:
Database preparation
create_tables.sql file:
CREATE TABLE [departments] (
[id] INT NOT NULL,
[department_name] VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
[location] VARCHAR(50) NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ([id])
);
CREATE TABLE [users] (
[id] INT IDENTITY(1,1),
[name] VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
[surname] VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
[department_id] INT,
PRIMARY KEY ([id]),
FOREIGN KEY ([department_id]) REFERENCES [departments] ([id])
);
insert_data.sql file:
INSERT INTO [departments]
([id], [department_name], [location])
VALUES
(1, 'Sales', 'New York'),
(2, 'Finance', NULL),
(3, 'HR', 'Atlanta'),
(4, 'Purchase', 'New Orlean'),
(5, 'Operations', 'Boston');
INSERT INTO [users]
( [name], [surname], [department_id])
VALUES
('John', 'Stewart', 1),
('Chris', 'Brown', 2),
('Kate', 'Lewis', 3),
('Ailisa', 'Gomez', NULL),
('Gwendolyn', 'James', 2),
('Simon', 'Collins', 4),
('Taylor', 'Martin', 2),
('Andrew', 'Thompson', NULL);