EN
MS SQL Server - Column name aliases
0
points
In this article, we would like to show you how to use aliases in MS SQL Server.
Quick solution:
SELECT [column_name] AS [alias_name]
FROM [table_name];
Aliases are used to give a table or a column in the table a temporary name to make it more readable. They only exist for the duration of a query.
We create aliases using AS keyword.
Practical example
To show how aliases work, we will use the following table:
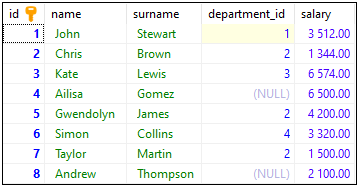
Note:
At the end of this article you can find database preparation SQL queries.
Example 1
In this example, we will display the average salary.
Query:
SELECT AVG([salary]) AS [average_salary]
FROM [users];
Output:
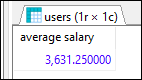
Example 2
In this example, we will display the number of users.
Query:
SELECT COUNT(*) AS [number_of_users]
FROM [users];
Output:
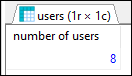
Database preparation
create_tables.sql file:
CREATE TABLE [users] (
[id] INT IDENTITY(1,1),
[name] VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
[surname] VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
[department_id] INT,
[salary] DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ([id])
);
insert_data.sql file:
INSERT INTO [users]
( [name], [surname], [department_id], [salary])
VALUES
('John', 'Stewart', 1, '3512.00'),
('Chris', 'Brown', 2, '1344.00'),
('Kate', 'Lewis', 3, '6574.00'),
('Ailisa', 'Gomez', NULL, '6500.00'),
('Gwendolyn', 'James', 2, '4200.00'),
('Simon', 'Collins', 4, '3320.00'),
('Taylor', 'Martin', 2, '1500.00'),
('Andrew', 'Thompson', NULL, '2100.00');