Java - create and write file
In this article, we would like to show you how to create and write files in Java.
There are several methods to create and write files in Java:
Files.newBufferedWriter(Java 8)Files.write(Java 7)FileOutputStream(Java 7)File.createNewFilePrintWriter
1. Files.newBufferedWriter
In this example, we use Files.newBufferedWriter() method to create a new example.txt file and write some text inside it. If the file already exists, the content will be overwritten.
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filename = "C:\\path\\example.txt";
Path path = Paths.get(filename);
// create and write to the example.txt file
try (BufferedWriter writer = Files.newBufferedWriter(path, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) {
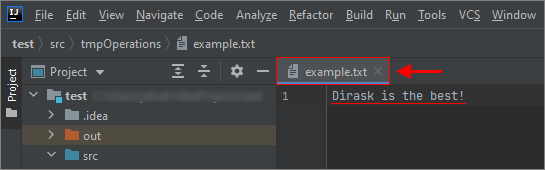
writer.write("Dirask is the best!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Result:
2. Files.write
In this example, we use Files.write() method to create a new example.txt file and write some text inside it. If the file already exists, the content will be overwritten.
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filename = "C:\\path\\example.txt";
String text = "Dirask is the best!";
// create and write to the example.txt file
try {
Files.write(
Paths.get(filename),
text.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Result:

3. FileOutputStream
In this example, we use FileOutputStream to create a new example.txt file and write some text inside it. If the file already exists, the content will be overwritten.
import java.io.*;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create and write to the example.txt file
try {
OutputStream file = new FileOutputStream("C:\\path\\example.txt");
String text = "Dirask is the best!";
// converts string into byte array
byte b[] = text.getBytes();
file.write(b);
file.close();
System.out.println("File write ended successfully.");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4. File.createNewFile
The File.createNewFile() method returns:
true- if the file doesn't exist and was created successfully,false- if the file is already exists
In this example, we use File.createNewFile method to create a new example.txt file and FileWriter to write some text inside it. If the file exists, the FileWriter will overwrite the content.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filename = "C:\\path\\example.txt";
// create example.txt file
try {
File file = new File(filename);
if (file.createNewFile()) {
System.out.println("File created successfully!");
} else {
System.out.println("File already exists.");
}
// write to file
try (FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file)) {
writer.write("Dirask is the best!");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Output:
File created successfully!
Result:

5. PrintWriter
In this example, we use PrintWriter class to create a new example.txt file and write some text inside it. If the file already exists, the content will be overwritten.
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filename = "C:\\path\\example.txt";
String text = "Dirask is the best!";
// create and write to the example.txt file
try (PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(filename, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) {
writer.println("line 1");
writer.println("line 2");
writer.println("line 3");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Result: