EN
Java - Math.log() method example
3
points
The Math.log() method returns the natural logarithm (base e) of a number.
public class MathExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Natural logarithm (logarithm with base e):
// x y
System.out.println( Math.log( 1 ) ); // 0
System.out.println( Math.log( 7 ) ); // 1.9459101490553132
System.out.println( Math.log( 10 ) ); // 2.3025850929940460
System.out.println( Math.log( 100 ) ); // 4.6051701859880920
System.out.println( Math.log( 1000 ) ); // 6.9077552789821370
System.out.println( Math.log( -1 ) ); // NaN
System.out.println( Math.log( 0 ) ); // -Infinity
System.out.println( Math.log( Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY ) ); // +Infinity
System.out.println( Math.E ); // 2.718281828459045
// Logarithm with custom base is placed in below example.
}
}
The Math.log() method is presented on the following chart:
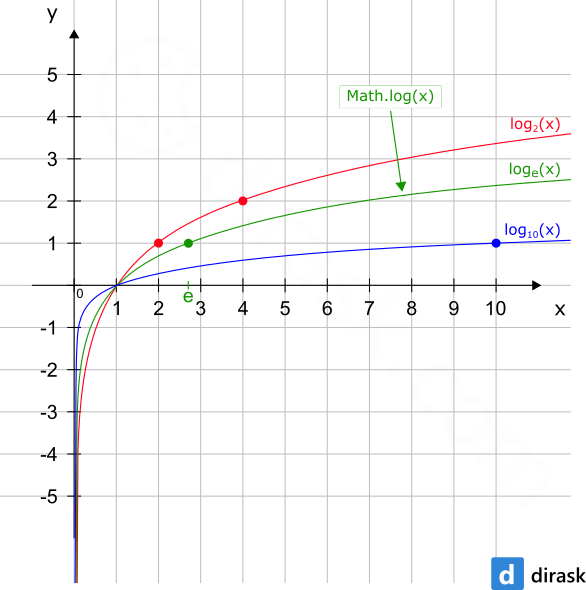
1. Documentation
| Syntax |
|
| Parameters | x - double value in the range 0 to +Infinitive (primitive value). |
| Result |
If If If |
| Description |
|
2. Logarithm with custom base example
This example shows a logarithmic function calculation with its own base.
public class MathExample {
static double calculateLogarithm(double base, double x) {
double a = Math.log(x);
double b = Math.log(base);
return a / b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Logarithm with custom base:
// base x y
System.out.println( calculateLogarithm( 2, 2 ) ); // 1.0
System.out.println( calculateLogarithm( 2, 4 ) ); // 2.0
System.out.println( calculateLogarithm( Math.E, Math.E ) ); // 1.0
System.out.println( calculateLogarithm( 3, 9 ) ); // 2.0
System.out.println( calculateLogarithm( 3, 81 ) ); // 4.0
System.out.println( calculateLogarithm( 10, 10 ) ); // 1.0
}
}