EN
PostgreSQL - INSERT INTO statement
3
points
In this article, we would like to show you how to use INSERT INTO statement in PostgreSQL.
Quick solution:
INSERT INTO "table_name"
("column1", "column2", "column3", ...)
VALUES
("value1", "value2", "value3", ...);
or:
INSERT INTO "table_name"
("column1", "column2", "column3", ...)
VALUES
("value1", "value2", "value3", ...),
("value1", "value2", "value3", ...),
("value1", "value2", "value3", ...),
...;
Practical example
To show how the INSERT INTO statement works, we will use the following table:
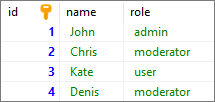
Note:
At the end of this article you can find database preparation SQL queries.
Example 1
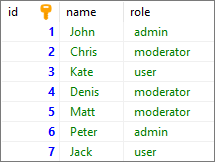
In this example, we will insert a new user (moderator) into the users table.
Query:
INSERT INTO "users" ("name", "role") VALUES ('Matt', 'moderator');
Output:
Example 2
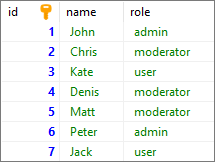
In this example, we will insert three new users into the users table.
Query:
INSERT INTO "users"
("name", "role")
VALUES
('Matt', 'moderator'),
('Peter', 'admin'),
('Jack', 'user');
Output:
Database preparation
create_tables.sql file:
CREATE TABLE "users" (
"id" SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
"name" VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
"role" VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL
);
insert_data.sql file:
INSERT INTO "users"
("name", "role")
VALUES
('John', 'admin'),
('Chris', 'moderator'),
('Kate', 'user'),
('Denis', 'moderator');