EN
Java - Math.PI property example
0
points
The Math.PI property returns π number (3.141592653589793...).
public class MathExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ------------------------------------------------------
// Math.PI value priting:
System.out.println( Math.PI ); // 3.141592653589793
// ------------------------------------------------------
// Math.PI with circle:
final double radius = 5;
// 1. Circle surface area:
double area = Math.PI * Math.pow(radius, 2);
System.out.println( area ); // 78.53981633974483
// 2. Circle circumference:
double circumference = 2 * Math.PI * radius;
System.out.println( circumference ); // 31.41592653589793
}
}
1. Documentation
| Syntax |
|
| Result | π number (3.141592653589793...). |
| Description |
|
2. Nilakantha series example
To calculate PI number Nilakantha series can be used.
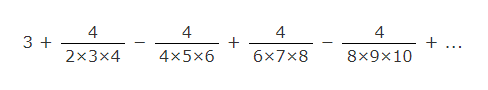
public class CustomMath {
static double computePi(int iterations) {
double approximation = 3;
double a = 2;
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++) {
approximation += 4 / (a * (++a) * (++a));
approximation -= 4 / (a * (++a) * (++a));
}
return approximation;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println( CustomMath.computePi( 1 )); // 3.1333333333333333
System.out.println( CustomMath.computePi( 2 )); // 3.1396825396825396
System.out.println( CustomMath.computePi( 5 )); // 3.1414067184965018
System.out.println( CustomMath.computePi( 10 )); // 3.141565734658547
System.out.println( CustomMath.computePi( 20 )); // 3.141589028940776
System.out.println( CustomMath.computePi( 50 )); // 3.1415924109719824
System.out.println( CustomMath.computePi( 100 )); // 3.141592622804848
System.out.println( CustomMath.computePi( 200 )); // 3.1415926497127264
System.out.println( CustomMath.computePi( 500 )); // 3.141592653340544
System.out.println( CustomMath.computePi( 1000 )); // 3.141592653558594
System.out.println( CustomMath.computePi( 2000 )); // 3.141592653585895
System.out.println( CustomMath.computePi( 5000 )); // 3.141592653589538
}
}