JavaScript - get entire document height
In this article, we're going to have a look at how to get the entire document height with JavaScript.
Quick solution (copy and paste in your source code):
// ONLINE-RUNNER:browser;
var htmlElement = document.documentElement;
var bodyElement = document.body;
var height = Math.max(
htmlElement.clientHeight, htmlElement.scrollHeight, htmlElement.offsetHeight,
bodyElement.scrollHeight, bodyElement.offsetHeight
);
console.log('entire document height: ' + height + 'px');
Note: read this article to know how to measture entire document width.
Practical example
The presented below solution is based on taking the biggest known height (clientHeight, HTML, or body element) to predict total page size. We assumed that: document, it is all client area with parts that overflow outside.
Quick solution:
// ONLINE-RUNNER:browser;
<!doctype html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Web page content here...</p>
<script>
var htmlElement = document.documentElement;
var bodyElement = document.body;
var height = Math.max( // <---------------------------- entire document height
htmlElement.clientHeight, htmlElement.scrollHeight, htmlElement.offsetHeight,
bodyElement.scrollHeight, bodyElement.offsetHeight
);
console.log('entire document height: ' + height + 'px');
</script>
</body>
</html>
Note: it is important to check height after
bodyelement is ready. So checking can be run afterbodyonloadevent occurred or made in somebodyscript.
Explanation
The reasons why Math.max() function is necessary are:
- client area can be bigger than the main dom elements,
- client area can be smaller than the main dom elements.
What was visualized below:
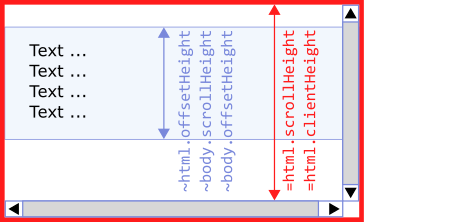
1. Case when html and body elements are smaller than the client part of the browser window.
~ at the beginning of the blue area, the description means: values are very close to themself. It is caused because of borders, margins, and nested body inside html element.
= at the beginning of the window, the description means: values are equal.
Run this code directly in your web browser to see the effect:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<body style="border: 5px solid red; height: 100px;">
<p>Web page content here...</p>
<script>
var html = document.documentElement;
var body = document.body;
console.log('html.clientHeight = ' + html.clientHeight);
console.log('html.scrollHeight = ' + html.scrollHeight);
console.log('html.offsetHeight = ' + html.offsetHeight);
console.log('body.scrollHeight = ' + body.scrollHeight);
console.log('body.offsetHeight = ' + body.offsetHeight);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Example output:
html.clientHeight = 969
html.scrollHeight = 969
html.offsetHeight = 126
body.scrollHeight = 100
body.offsetHeight = 110
Where:
html.scrollHeight == html.clientHeight == 969- height of the client area of the web browser windowhtml.offsetHeight == 126- height of HTML (contains inside: body with margins)body.scrollHeight == 100- potentially scrollable area inside the body (without borders)body.offsetHeight == 110- body height + 2x border width (top + bottom)
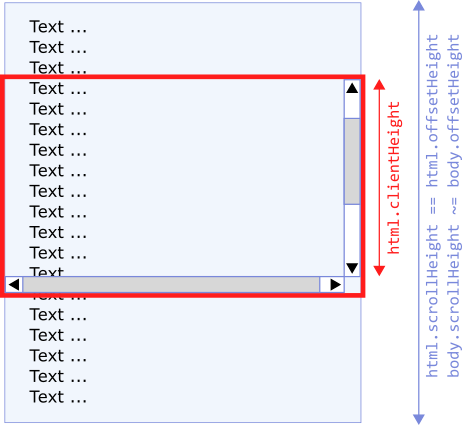
2. Case when html and body elements are bigger than the client part of the web browser window.
== means: values are equal.
~= means: values are very close to themself. It is caused because of borders, margins, and nested body inside html element.
Run this code directly in your web browser to see the effect:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<body style="border: 5px solid red; height: 4000px;">
<p>Web page content here...</p>
<script>
var html = document.documentElement;
var body = document.body;
console.log('html.clientHeight = ' + html.clientHeight);
console.log('html.scrollHeight = ' + html.scrollHeight);
console.log('html.offsetHeight = ' + html.offsetHeight);
console.log('body.scrollHeight = ' + body.scrollHeight);
console.log('body.offsetHeight = ' + body.offsetHeight);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Example output:
html.clientHeight = 969
html.scrollHeight = 4026
html.offsetHeight = 4026
body.scrollHeight = 4000
body.offsetHeight = 4010
Where:
html.clientHeight == 969- height of the client area of the web browser windowhtml.scrollHeight == html.offsetHeight == 4026- all HTML element is scrolled (contains inside: body with border and margins)body.scrollHeight == 4000- potentially scrollable area inside the body (without borders)body.offsetHeight == 4010- body height + 2x border width (top + bottom)