JavaScript - what is the difference between == and === operators?
In JavaScript, there are available four different operators for checking two values are equal or not: ==, !=, === and !==. In this article, we will try to describe differences between them.
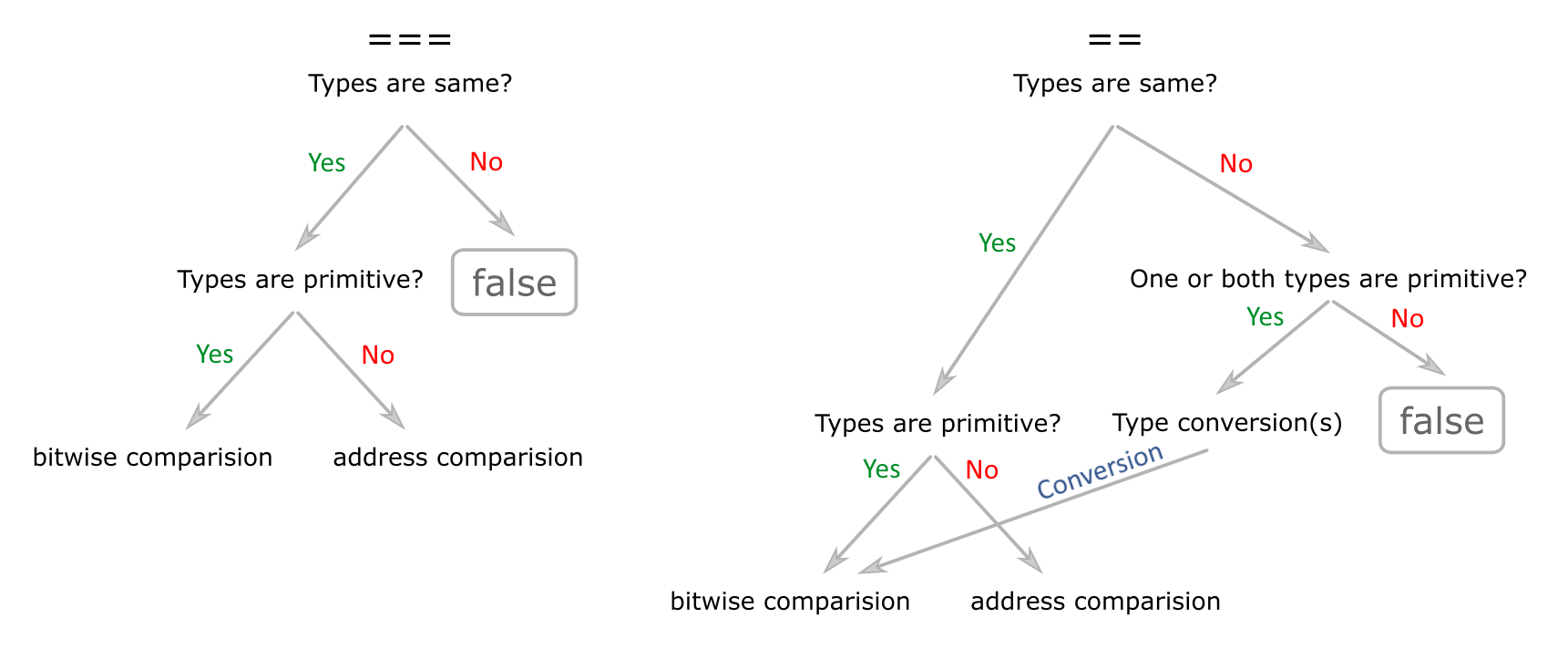
1. What is the difference between identity and equality operators (== vs ===) ?
Identity operator (===) works similar to equality operator (==) except variable type comparison - equality operator does not do it. Equality operator converts types if it is necessary and later chceck values - it manes to use this operator it is necessary to have knowledge about automatic types conversion because sometimes conversion result is not obvious. Identity operator starts with type comparision and later if they are same makes comparision.
2. Which operator should be used?
It is the most commonly asked question.
The answer to this question is: Identity operator (===) should be used to avoid errors - it is a JSLint suggestion too.
A simple case showing why an identity operator should be used has been presented below:
// ONLINE-RUNNER:browser;
console.log( 25 === [25] ); // false
console.log( 25 == [25] ); // true
Note: in above example we can see the knowledge about used type is important - programmer making mistake ([25] - array with one element) can affect program will be working still correctly.
Solution: using identity operator.
3. JavaScript equality table example
The below material comes from GitHub.
Authtor put suggestion: Always use 3 equals unless you have a good reason to use 2.
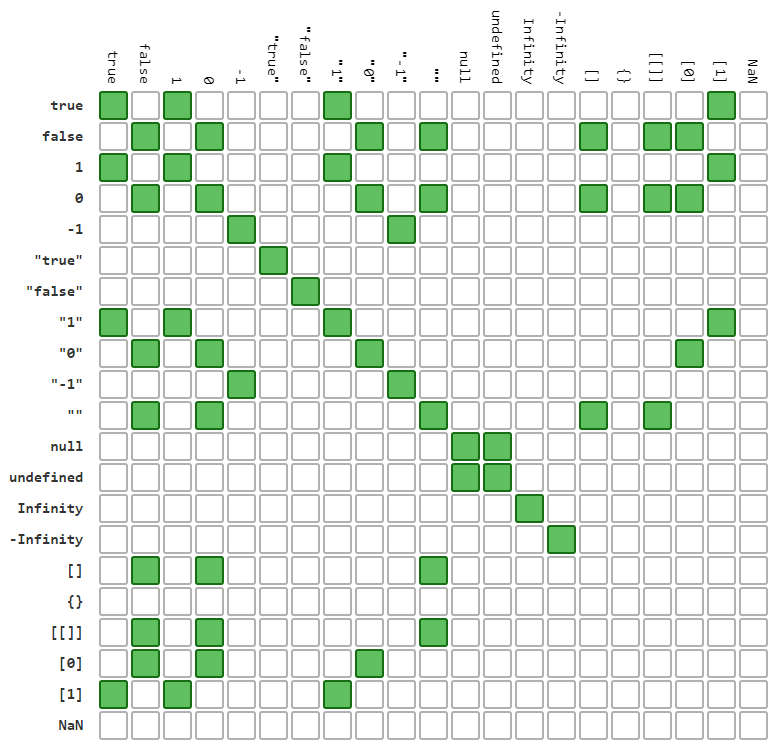
3.1. == and != comparison result
green means result for == is true (for != false)
white means result for != is true (for == false)
== operator result for different values / objects comparision:
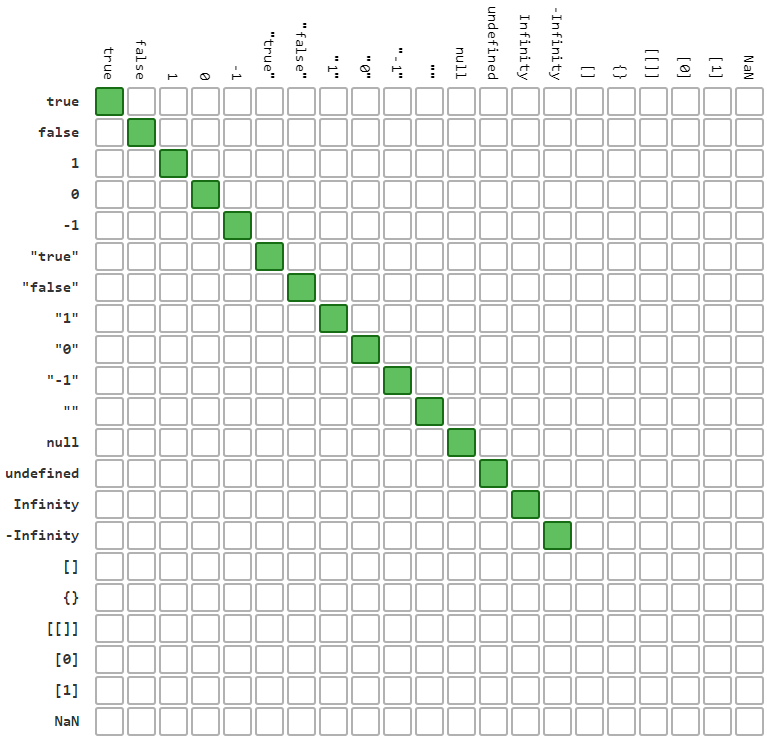
3.1. === and !== comparison result
green means result for === is true (for !== false)
white means result for !== is true (for === false)
=== operator result for different values / objects comparision: