EN
Spring Boot + Spring Data JPA + H2 - unit tests simple example - @DataJpaTest
4
points
Full and tested example of how to use Spring Boot + Spring Data JPA + H2 when writing unit tests.
Github repository with this example:
Download this example:
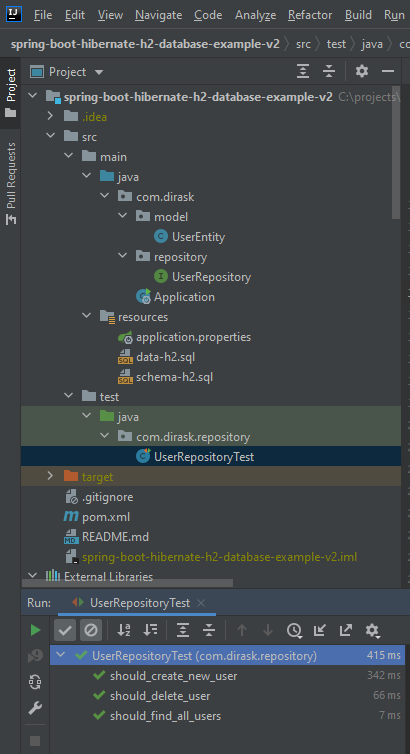
Project structure:
UserEntity.java
package com.dirask.model;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.util.Objects;
@Entity
@Table(name = "users")
public class UserEntity {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
private int age;
public UserEntity() {
}
public UserEntity(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
UserEntity user = (UserEntity) o;
return age == user.age && Objects.equals(id, user.id) && Objects.equals(name, user.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, name, age);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
UserRepository.java
package com.dirask.repository;
import com.dirask.model.UserEntity;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends CrudRepository<UserEntity, Long> {
UserEntity findOneByName(String name);
}
Application.java
package com.dirask;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
application.properties
spring.main.banner-mode=off
spring.datasource.platform=h2
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=none
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
data-h2.sql
INSERT INTO users(name, age) VALUES('Kate', 26);
schema-h2.sql
CREATE TABLE `users` (
`id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(255) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`age` INT(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
UserRepositoryTest.java
package com.dirask.repository;
import com.dirask.model.UserEntity;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.DataJpaTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@DataJpaTest
public class UserRepositoryTest {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Test
public void should_create_new_user() {
UserEntity user = new UserEntity("Tom", 25);
userRepository.save(user);
UserEntity userByName = userRepository.findOneByName("Tom");
assertThat(userByName).isNotNull();
// User{id=2, name='Tom', age=25}
System.out.println(userByName.toString());
}
@Test
public void should_find_all_users() {
Iterable<UserEntity> users = userRepository.findAll();
assertThat(users).hasSize(1);
}
@Test
public void should_delete_user() {
UserEntity userByName = userRepository.findOneByName("Kate");
assertThat(userByName).isNotNull();
userRepository.delete(userByName);
Iterable<UserEntity> users = userRepository.findAll();
assertThat(users).hasSize(0);
}
}