EN
Node.js - PostgreSQL - select last N rows
0
points
In this article, we would like to show you how to select the last N rows in the PostgreSQL database using Node.js.
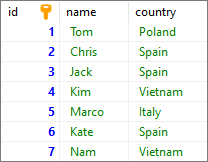
Note: at the end of this article you can find database preparation SQL queries.
Ascending order
const { Client } = require('pg');
const client = new Client({
host: '127.0.0.1',
user: 'postgres',
database: 'database_name',
password: 'password',
port: 5432,
});
const getLastUsers = async (count) => {
const query = `
SELECT * FROM (
SELECT * FROM "users"
ORDER BY "id" DESC
LIMIT $1
) subquery
ORDER BY "id" ASC;
`;
try {
await client.connect(); // gets connection
const { rows } = await client.query(query, [count]); // sends query
console.table(rows);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error.stack);
} finally {
await client.end(); // closes connection
}
};
getLastUsers(3); // get last 3 users in ascending order
Result:
┌─────────┬────┬─────────┬───────────┐
│ (index) │ id │ name │ country │
├─────────┼────┼─────────┼───────────┤
│ 0 │ 5 │ 'Marco' │ 'Italy' │
│ 1 │ 6 │ 'Kate' │ 'Spain' │
│ 2 │ 7 │ 'Nam' │ 'Vietnam' │
└─────────┴────┴─────────┴───────────┘
Descending order
const { Client } = require('pg');
const client = new Client({
host: '127.0.0.1',
user: 'postgres',
database: 'database_name',
password: 'password',
port: 5432,
});
const getLastUsers = async (count) => {
const query = `SELECT *
FROM "users"
ORDER BY "id" DESC
LIMIT $1;`;
try {
await client.connect(); // gets connection
const { rows } = await client.query(query, [count]); // sends query
console.table(rows);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error.stack);
} finally {
await client.end(); // closes connection
}
};
getLastUsers(3); // get last 3 users in descending order
Result:
┌─────────┬────┬─────────┬───────────┐
│ (index) │ id │ name │ country │
├─────────┼────┼─────────┼───────────┤
│ 0 │ 7 │ 'Nam' │ 'Vietnam' │
│ 1 │ 6 │ 'Kate' │ 'Spain' │
│ 2 │ 5 │ 'Marco' │ 'Italy' │
└─────────┴────┴─────────┴───────────┘
Database preparation
create_tables.sql file:
CREATE TABLE "users" (
"id" SERIAL,
"name" VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
"country" VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ("id")
);
insert_data.sql file:
INSERT INTO "users"
("name", "country")
VALUES
('Tom', 'Poland'),
('Chris', 'Spain'),
('Jack', 'Spain'),
('Kim', 'Vietnam'),
('Marco', 'Italy'),
('Kate', 'Spain'),
('Nam', 'Vietnam');
Native SQL query (used in the above example):
Ascending order
SELECT * FROM (
SELECT * FROM `users`
ORDER BY `id` DESC
LIMIT 3
) subquery
ORDER BY `id` ASC;
Descending order
SELECT *
FROM `users`
ORDER BY `id` DESC
LIMIT 3;