PL
Spring Boot 2 - umieszczanie zmiennych w ścieżce (@PathVariable)
6
points
Celem tego artykułu jest pokazanie, jak w prosty sposób można umieszczać zmienne w ścieżce w adresie URL w aplikacji Spring Boot.
Jako zmienne w ścieżce w adresie URL rozumiemy konstrukcję:
/path/to/endpoint/{name1}/{name2}/{nameN}
Co w praktyce może mieć formę:
https://some-domain.com/path/to/endpoint/value1/value2/valueN
Gdzie:
- zmienne należy umieszczać w
{ }, - ilość zmiennych może być dowolna,
- zmienne mogą znajdować się w dowolnych miejscach ścieżek,
- przekazywane zmienne to:
Nazwa zmiennej Wartość zmiennej name1value1name2value2nameNvalueN
Praktyczny przykład
W Spring Boot możemy takie zmienne przekazywać jako argumenty do metody z mapowaniem, gdy użyjemy adnotacji @PathVariable koło argumentów.
Przykład użycia mapowania:
Przykładowy kod kontrolera:
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class HomeController {
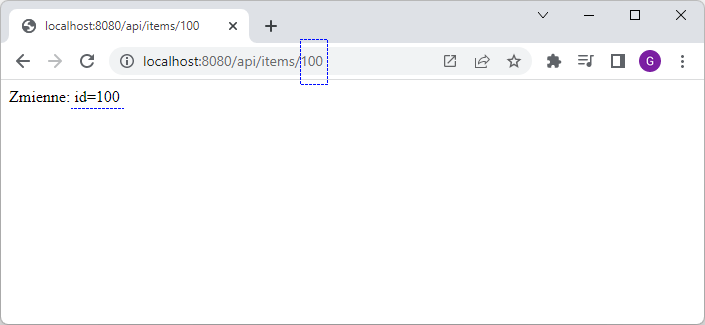
// http://localhost:8080/api/items/100
//
@RequestMapping("/api/items/{id}")
@ResponseBody
public Object getItems(@PathVariable Long id) {
return "Zmienne: id=" + id;
}
}
Konfiguracja parametrów
Za pomocą konfiguracji w @PathVariable możemy:
- ustawić czy zmienna ma być wymagana,
np.required=truelubrequired=falseUwagi:
- domyślnie zmienne są wymagane (
required=true), - niewymagana zmienna posiada wartość
null(required=false).
- domyślnie zmienne są wymagane (
- mapować różne nazwy zmiennych na różne nazwy argumentów,
np.name="variable-name"
Przykład użycia mapowania:
Przykładowy kod kontrolera:
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class HomeController {
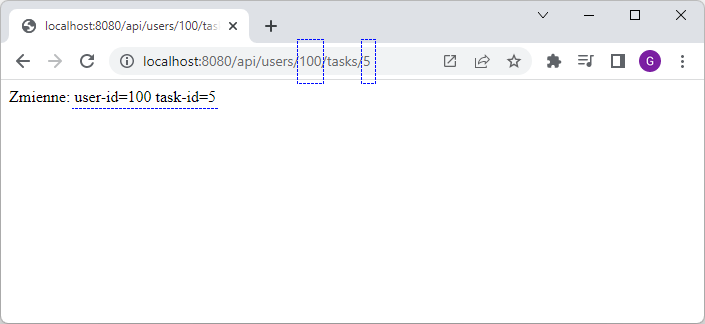
// http://localhost:8080/api/users/100/tasks
// http://localhost:8080/api/users/100/tasks/5
//
@RequestMapping({"api/users/{user-id}/tasks", "/api/users/{user-id}/tasks/{task-id}"})
@ResponseBody
public Object getUserTask(
@PathVariable(name = "user-id" ) Long userId,
@PathVariable(name = "task-id", required = false ) Integer taskId
) {
return "Zmienne: user-id=" + userId + " task-id=" + taskId;
}
}
Uwaga: aby używać niewymaganych zmiennych w ścieżce, należy zawsze zdefiniować alternatywne mapowanie niewymagające danej zmiennej - w powyższym przykładzie tak zrobiono dla zmiennej
taks-id.
Alternatywny kod kontrolera:
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class HomeController {
// http://localhost:8080/api/users/100/tasks
//
@RequestMapping("api/users/{user-id}/tasks")
@ResponseBody
public Object getUserTasks(@PathVariable(name = "user-id") Long userId) {
return "Zmienne: user-id=" + userId;
}
// http://localhost:8080/api/users/100/tasks/5
//
@RequestMapping("/api/users/{user-id}/tasks/{task-id}")
@ResponseBody
public Object getUserTask(
@PathVariable(name = "user-id" ) Long userId,
@PathVariable(name = "task-id", required = false ) Integer taskId
) {
return "Zmienne: user-id=" + userId + " task-id=" + taskId;
}
}