Python - math.atan2() method example
The math.atan2() function returns the angle in radians in the range -math.pi/2 to +math.pi/2 between the positive x-axis and the ray to the point (x, y) ≠ (0, 0).
import math
# y x angle in radians
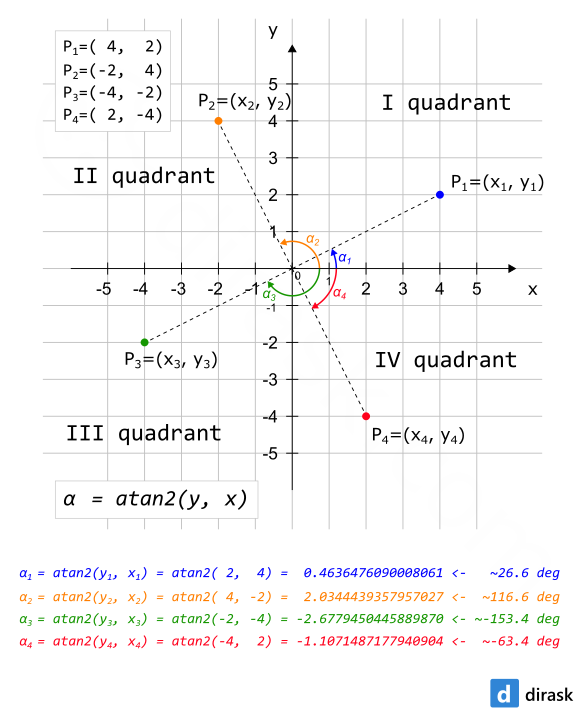
print(math.atan2(2, 4)) # 0.4636476090008061 <- ~26.6 degrees
print(math.atan2(4, -2)) # 2.0344439357957027 <- ~116.6 degrees
print(math.atan2(-2, -4)) # -2.677945044588987 <- ~-153.4 degrees
print(math.atan2(-4, 2)) # -1.1071487177940904 <- ~-63.4 degrees
atan2() method has been visualized on below image:
1. Documentation
| Syntax |
|
| Parameters | y, x - double values that are coordinates of the point. |
| Result |
Where:
If point is in the 1st (I) or 2nd (II) quadrant angle is measured in a counterclockwise direction. If point is in the 3rd (III) or 4th (IV) quadrant angle is measured in a clockwise direction.
|
| Description |
|
2. Working with degrees
import math
def calculate_angle(x, y):
angle = math.atan2(x, y)
return (180 / math.pi) * angle
# y x degrees
print(calculate_angle(2, 4)) # 26.56505117707799
print(calculate_angle(4, -2)) # 116.56505117707799
print(calculate_angle(-2, -4)) # -153.434948822922
print(calculate_angle(-4, 2)) # -63.43494882292201
3. Conversion to only clockwise angles in degrees
This section shows how to convert angles to clockwise angles (from 0 to 360 degrees).
import math
def calculate_angle(x, y):
angle = math.atan2(x, y)
if angle < 0:
angle += 2 * math.pi
return (180 / math.pi) * angle
# y x degrees
print(calculate_angle(2, 4)) # 26.56505117707799
print(calculate_angle(4, -2)) # 116.56505117707799
print(calculate_angle(-2, -4)) # 206.565051177078
print(calculate_angle(-4, 2)) # 296.565051177078
4. Conversion to only counterclockwise angles in degrees
This section shows how to convert angles to counterclockwise angles (from -360 to 0 degrees).
import math
def calculate_angle(x, y):
angle = math.atan2(x, y)
if angle > 0:
angle -= 2 * math.pi
return (180 / math.pi) * angle # rad to deg conversion
# y x degrees
print(calculate_angle(2, 4)) # -333.434948822922
print(calculate_angle(4, -2)) # -243.434948822922
print(calculate_angle(-2, -4)) # -153.434948822922
print(calculate_angle(-4, 2)) # -63.43494882292201