EN
PostgreSQL - UPPER() function example
0
points
In this article, we would like to show you how to use UPPER() function in PostgreSQL.
Quick solutions:
SELECT UPPER('some text...');
SELECT UPPER("column_name") FROM "table_name";
Practical example
To show how the UPPER() function works, we will use the following table:
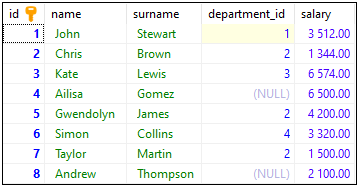
Note:
At the end of this article you can find database preparation SQL queries.
Example
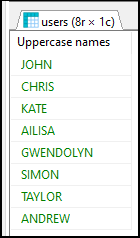
In this example, we will display all the names from users table in uppercase.
Query:
SELECT UPPER("name") AS "Uppercase names" FROM "users";
Output:
Database preparation
create_tables.sql file:
CREATE TABLE "users" (
"id" SERIAL,
"name" VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
"surname" VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
"department_id" INTEGER,
"salary" DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ("id")
);
insert_data.sql file:
INSERT INTO "users"
( "name", "surname", "department_id", "salary")
VALUES
('John', 'Stewart', 1, '3512.00'),
('Chris', 'Brown', 2, '1344.00'),
('Kate', 'Lewis', 3, '6574.00'),
('Ailisa', 'Gomez', NULL, '6500.00'),
('Gwendolyn', 'James', 2, '4200.00'),
('Simon', 'Collins', 4, '3320.00'),
('Taylor', 'Martin', 2, '1500.00'),
('Andrew', 'Thompson', NULL, '2100.00');