EN
MS SQL Server - add index to existing table using CREATE INDEX
0
points
TODO: indexy na koniec
In this article, we would like to show you how to add index to an existing table using CREATE INDEX statement in MS SQL Server.
Quick solution:
CREATE INDEX [index_name]
ON [table_name] ([column1], [column2], [columnN]);
Practical example
To show how the CREATE INDEX statement works, we will use the following table:
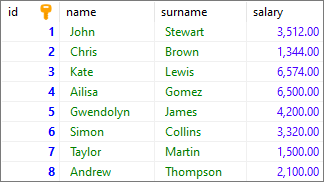
Note:
At the end of this article you can find database preparation SQL queries.
Example 1 - one column index
In this example, we will create an index for the salary column in users table.
Query:
CREATE INDEX [salary_index]
ON [users] ([salary]);
Result:
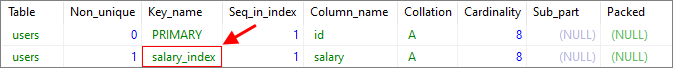
1. Using query
SHOW INDEX FROM [users] FROM [dirask]; -- where users-table_name, dirask-database_name
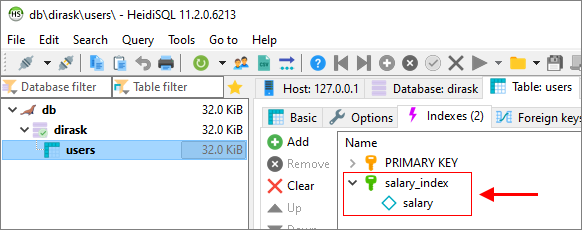
2. Using HeidiSQL
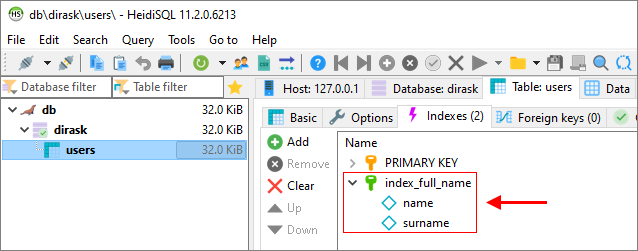
Example 2 - two column index
In this example, we will create an index on the name and surname columns in users table.
Query:
CREATE INDEX [full_name_index]
ON [users] ([name], [surname]);
Result:
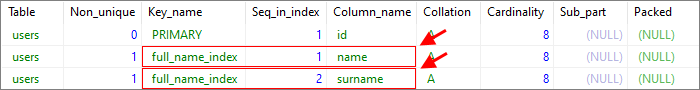
1. Using query
SHOW INDEX FROM [users] FROM [dirask]; -- where users-table_name, dirask-database_name
2. Using HeidiSQL
Database preparation
create_tables.sql file:
CREATE TABLE [users] (
[id] INT IDENTITY(1,1),
[name] VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
[surname] VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
[salary] DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ([id])
);
insert_data.sql file:
INSERT INTO [users]
( [name], [surname], [salary])
VALUES
('John', 'Stewart', '3512.00'),
('Chris', 'Brown', '1344.00'),
('Kate', 'Lewis', '6574.00'),
('Ailisa', 'Gomez', '6500.00'),
('Gwendolyn', 'James', '4200.00'),
('Simon', 'Collins', '3320.00'),
('Taylor', 'Martin', '1500.00'),
('Andrew', 'Thompson', '2100.00');