EN
JavaScript - Math.log() method example
9
points
The Math.log() method returns the natural logarithm (base e) of a number.
// ONLINE-RUNNER:browser;
// x y
console.log( Math.log( 1 ) ); // 0
console.log( Math.log( 7 ) ); // 1.9459101490553132
console.log( Math.log( 10 ) ); // 2.3025850929940460
console.log( Math.log( 100 ) ); // 4.6051701859880920
console.log( Math.log( 1000 ) ); // 6.9077552789821370
console.log( Math.log( -1 ) ); // NaN
console.log( Math.log( 0 ) ); // -Infinity
console.log( Math.log( +Infinity ) ); // +Infinity
console.log( Math.E ); // 2.718281828459045
// Logarithm with custom base is placed in the below example.
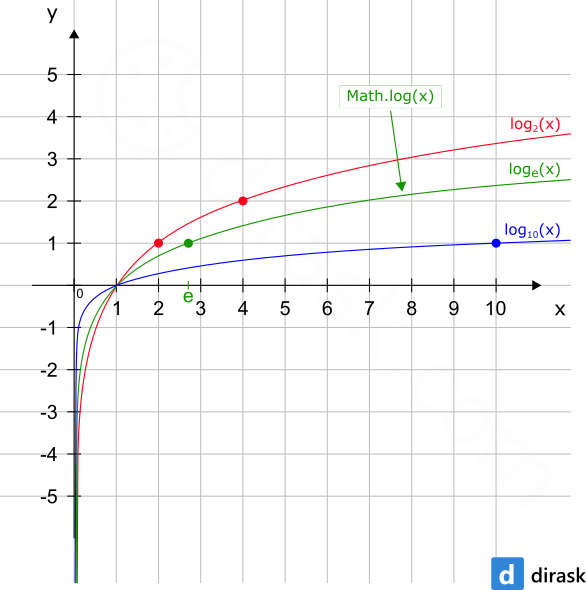
The Math.log() method is presented on the following chart:
1. Documentation
| Syntax | Math.log(x) |
| Parameters | x - integer or float number value in range 0 to +Infinitive (primitive value). |
| Result |
If If If |
| Description |
|
2. Logarithm with custom base example
This example shows a logarithmic function calculation with own base.
// ONLINE-RUNNER:browser;
function calculateLogarithm(base, x) {
var a = Math.log(x);
var b = Math.log(base);
return a / b;
}
// Logarithm with custom base:
// base x y
console.log( calculateLogarithm( 2, 2 ) ); // 1
console.log( calculateLogarithm( 2, 4 ) ); // 2
console.log( calculateLogarithm( Math.E, Math.E ) ); // 1
console.log( calculateLogarithm( 3, 9 ) ); // ~2
console.log( calculateLogarithm( 3, 81 ) ); // ~4
console.log( calculateLogarithm( 10, 10 ) ); // 1
3. Canvas plot example
// ONLINE-RUNNER:browser;
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<style> #canvas { border: 1px solid black; } </style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas>
<script>
var canvas = document.querySelector('#canvas');
var context = canvas.getContext('2d');
// logarithm chart range
var x1 = 0;
var x2 = 10;
var y1 = -5;
var y2 = 4;
var dx = 0.005;
var xRange = x2 - x1;
var yRange = y2 - y1;
function calculateLogarithm(base, x) {
var a = Math.log(x);
var b = Math.log(base);
return a / b;
}
function calculatePoint(base, x) {
var y = calculateLogarithm(base, x);
// chart will be reversed horizontaly because of reversed canvas pixels
var nx = (x - x1) / xRange; // normalized x
var ny = 1.0 - (y - y1) / yRange; // normalized y
var point = {
x: nx * canvas.width,
y: ny * canvas.height
};
return point;
}
function drawChart(base, color, thickness) {
var point = calculatePoint(base, x1);
context.beginPath();
context.lineWidth = thickness;
context.strokeStyle = color;
context.moveTo(point.x, point.y);
for (var x = x1 + dx; x < x2; x += dx) {
point = calculatePoint(base, x);
context.lineTo(point.x, point.y);
}
point = calculatePoint(base, x2);
context.lineTo(point.x, point.y);
context.stroke();
}
console.log('log_2(x) <- red');
console.log('log_e(x) <- green');
console.log('log_10(x) <- blue');
// base color thickness
drawChart( 2, '#ff001b', 0.8 ); // red
drawChart( Math.E, '#159600', 2 ); // green
drawChart( 10, '#0000ff', 0.8 ); // blue
console.log('x range: <' + x1 + '; ' + x2 + '>');
console.log('y range: <' + y1 + '; ' + y2 + '>');
</script>
</body>
</html>