PL
C# - przykład użycia Entity Framework wraz z Microsoft SQL Server
0
points
Celem tego artykułu jest pokazanie, jak w prosty sposób można tworzyć aplikację konsolową .NET, która komunikuje się z bazą danych przy użyciu Entity Framework, znajdującą się na serwerze Microsoft SQL.
Wykonaj kroki
- Utwórz projekt konsolowy typu .NET (np. wersja 5 lub 6).
- Dodaj do projektu referencje do
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer:Uwaga: pod tym linkiem znajdziesz instrukcję jak zainstalować i załączyć Entity Framework (5 lub 6 zależnie od .NET)
- Umieść w projekcie 2 pliki
- Dodaj plik
Model.cs:using System.Collections.Generic; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; public class BloggingContext : DbContext { public DbSet<Blog> Blogs { get; set; } public DbSet<Post> Posts { get; set; } public string ConnectionString { get; } public BloggingContext(string connectionString) { this.ConnectionString = connectionString; } protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder options) { options.UseSqlServer(this.ConnectionString); } } public class Blog { public long Id { get; set; } public string Url { get; set; } public List<Post> Posts { get; } = new(); } public class Post { public long Id { get; set; } public string Title { get; set; } public string Content { get; set; } public long BlogId { get; set; } public Blog Blog { get; set; } } - Dodaj plik
Program.cs:using System; using System.Linq; public class Program { public static void Main() { // Hint: change `DESKTOP-123ABC\SQLEXPRESS` to your server name // alternatively use `localhost` or `localhost\SQLEXPRESS` string connectionString = @"Data Source=DESKTOP-123ABC\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=blogdb;Integrated Security=True"; using (BloggingContext db = new BloggingContext(connectionString)) { Console.WriteLine($"Database ConnectionString: {db.ConnectionString}."); // Create Console.WriteLine("Inserting a new blog"); db.Add(new Blog { Url = "http://blogs.msdn.com/adonet" }); db.SaveChanges(); // Read Console.WriteLine("Querying for a blog"); Blog blog = db.Blogs .OrderBy(b => b.Id) .First(); // Update Console.WriteLine("Updating the blog and adding a post"); blog.Url = "https://devblogs.microsoft.com/dotnet"; blog.Posts.Add(new Post { Title = "Hello World", Content = "I wrote an app using EF Core!" }); db.SaveChanges(); // Delete Console.WriteLine("Delete the blog"); db.Remove(blog); db.SaveChanges(); } } }
- Dodaj plik
- Używając SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS):
Wskazówki:
- Nawiąż połączenie z serwerem SQL.
- Utwórz nową bazę danych nazwie
blogdb. - Utwórz nowe tabele o nazwach
BlogsiPostsi połącz je relacjami.
Przykładowe zapytanie SQL:USE [blogdb] GO CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Blogs] ( [Id] BIGINT IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [Url] NVARCHAR(4000) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY ([Id]) ); GO CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Posts] ( [Id] BIGINT IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [Title] NVARCHAR(200) NOT NULL, [Content] NVARCHAR(MAX) NOT NULL, [BlogId] BIGINT NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY ([Id]) ); GO ALTER TABLE [dbo].[Posts] ADD CONSTRAINT FK_Posts_Blogs FOREIGN KEY (BlogId) REFERENCES [dbo].[Blogs] (Id) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE; GO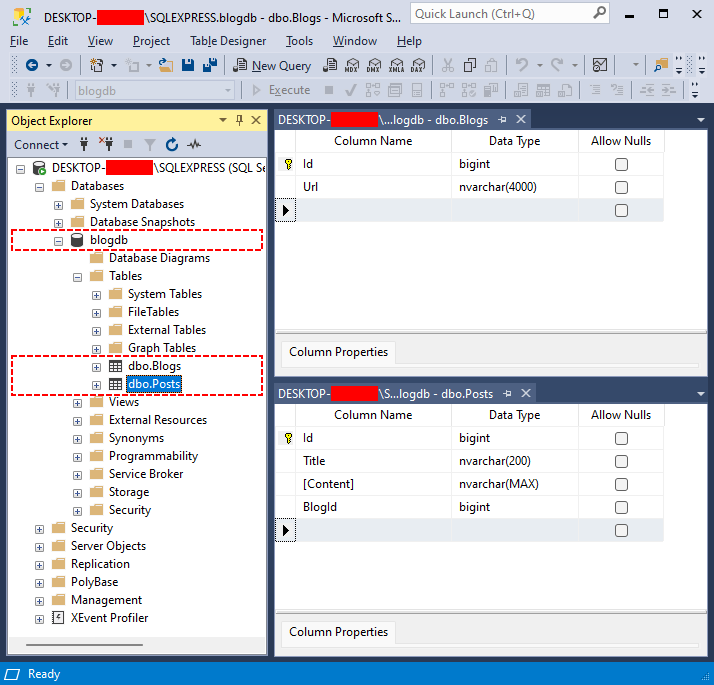
Przykładowa baza danych MS SQL.
- Uruchom aplikację i sprawdź, czy dostałeś następujące wyniki w konsoli:
Database ConnectionString: Data Source=DESKTOP-123ABC\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=blogdb;Integrated Security=True. Inserting a new blog Querying for a blog Updating the blog and adding a post Delete the blog